History of Zinc
Zinc is one of the elements, which was used as alloy with copper especially in brass; it is unknown precisely when zinc was produced. Brass was an alloy with tin that can be produced with small quantity of zinc. Brass was produced probably first time in Persia. The first trace of brass material was found in Lorestan in Iran in 500-2500 B.C. and conducted test showed that it contained 15-18% Zn. In 3500B.C. in Cyprium a brass was found with 5-8% Zn. There is no evidence or information on how the alloy was produced.
Before 1500 A.D. the Chinese and Indians knew of zinc as a metal in its own right. There is evidence that in India, at Zawar in Rajasthan, the metal was produced on a considerable scale in the fourteenth century. The method was used in Indian called Koshti (fig1).
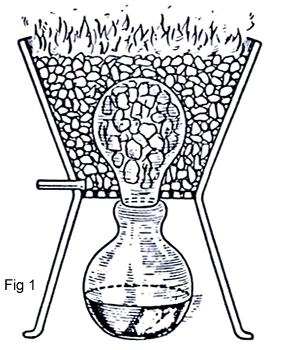
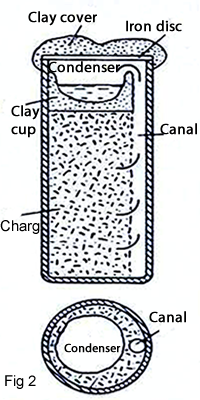
By this process the zinc ore and an organic substance were mixed and put into a crucible .The crucible was heated as figure 1 shows. Zinc was condensed and collected in the glass cup as molten material. It seems that The Indians could not produce Zinc in an industry scale in this form and this method was only used for medical purposes. It is not known exactly when Chinese started producing Zinc. However it is certain that the Chinese were aware of the zinc production before the Christian era. At the beginning of the Ming dynasty (1368 -1644) zinc coins were in circulation (99%Zn and 1%Cu).The technology of chinese was retorts. On a small scale; clay retorts were used 31 cm long, 12 cm diameter which were filled with a mixture of Zinc ore and anthracite. At the top of each retort luted a clay cup to act as a container for the zinc condensed and a crucible –shaped extension which was covered with an iron disc (fig2).These retorts were placed in a furnace and the process would be started. Until the year 1600 zinc was imported from Asia to Portugal, Germany and other European countries.
Germans called it Zink from zinke (the tooth of comb), itself derived from Zacke from jagged appearance of the ore of deposits. It is possible that the word "zinc" is derived from Persian word Seng meaning stone. English and French called it Zinc, Italians and Portuguese called it Zinco and Spanish called it Zinc or Cinc. Georius Agricola (1494-1555), in his important De re metallica, describes how the material found in large quantities in the eastern Alps was called "Zinc" by the local people. In 1550 the mining of lead and zinc was explored in Goslar (Germany). In 1718 Stahl considered that Smithsonite added a metallic to the copper during brass production. In 1746 in Berlin Marggraf produced zinc by distilling smithsonite in sealed vessels. He described his process as the "basic theory of zinc production".
The first industrial production of zinc began in England in about 1720. Probably based on knowledge from Asia; A process adapted from brass production to produce zinc by distillation. It is believed based on this knowledge a zinc factory was built in Bristol in 1743, with a capacity of more than 200 t/a zinc production. Ruberg developed the horizontal retort process for the production zinc in Germany. This process was used in 1798 in Wessola in Upper Siesia. The row material for this process was galmei but later used the smithsonite by using the roasting process. The rich zinc ore deposits are located in the USA. The zinc production began in USA from about 1840 and by 1907 USA was the world's leading producer of zinc .An important development in zinc production was achieved in 1930 at the New Jersey. This company develop the vertical retort which was economical in the zinc production industries.

