TiAl
Titanium aluminide intermetallic compounds are a new class of advanced materials with unique thermal properties such as high specific strength, excellent oxidation resistance and acceptable mechanical properties at high temperatures. This alloy has a wide range of application for example in the aerospace, automotive and turbine power generation industries .
The mechanical properties of TiAl alloy are sensitive to its microstructure. The variation in microstructure that can be controlled these alloys are numerous but they can perhaps divided in four different categories; near γ, duplex (DP), near lamellar (NL) and fully lamellar (FL) microstructures. These structures can be formed via heat treatment and alloying process. DP and FL macrostructure are two typical microstructures and have been subjected to more study than another two types.
Today is tendency on optimizing the fully lamellar structure of γ alloys to have a fine grain size because such structure is known to have better balanced properties than the Fl structure with a large grain size and the DP one with a fine grain size Figures 1and 2
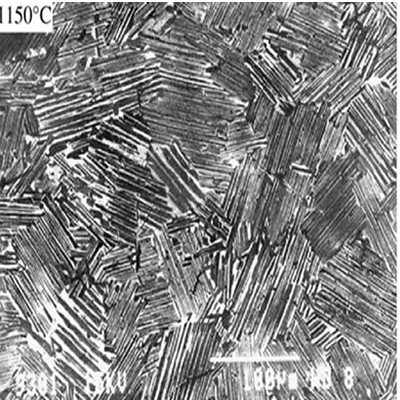
Fig 1 Typical lamellar grains of Ti-46.5Al-2W-05Si with heat treatment of 1150 0C
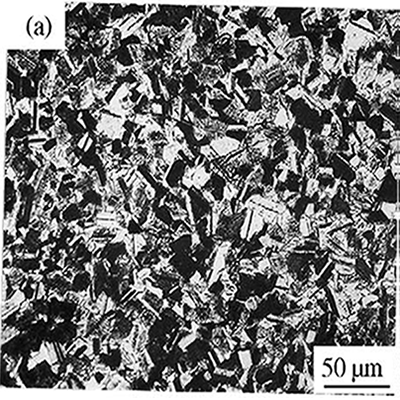
Fig 2 Typical duplex microstructures of Ti–47Al–2Cr (at.%) with conventional heat treatment and two-step heat treatment (1250 0C, 4 h, + 900 0C, 24 h)
The major concern for structure use of TiAl alloy is low ductility at room temperature. Adding such element as Cr ,B, C, Si, W ,Cr Mo and ,Nb can improved the mechanical properties of TiAl. At the same time, adjusting the microstructure of TiAl alloy by controlling heat treatment processing is another way to improve its mechanical properties specially its ductility.

