Cristal Structure
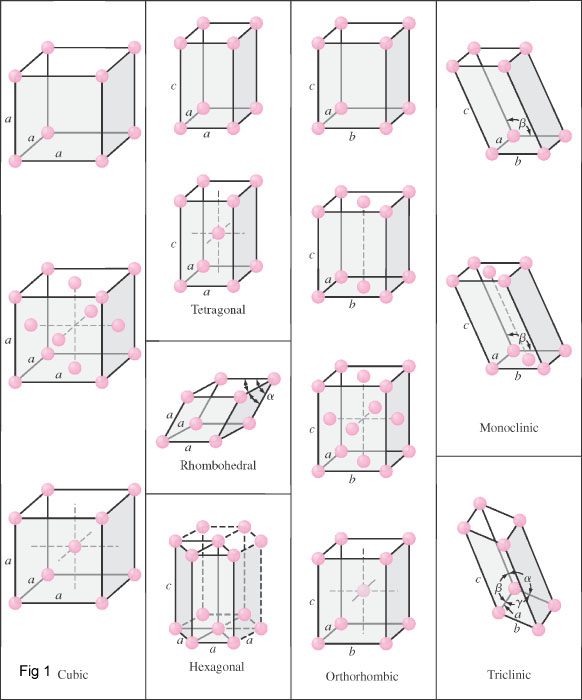
A crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. The atoms in a crystal are in a regular repeating unit cells called the crystalline lattice. Atomic arrangements in crystalline solids can be described with respect to a network of lines in three dimensions. The intersections of the lines are called "lattice sites" (or lattice points). Each lattice site has the same environment in the same direction. Lattice Points can be arranged in only 14 different arrays called Bravais lattice (fig 1),therefore the atoms in any crystal structure must be in positions designed by 1 of the 14.It is important to note that more than one atom can be associated with each lattice point. The lattice can have a profound influence on the material's properties.
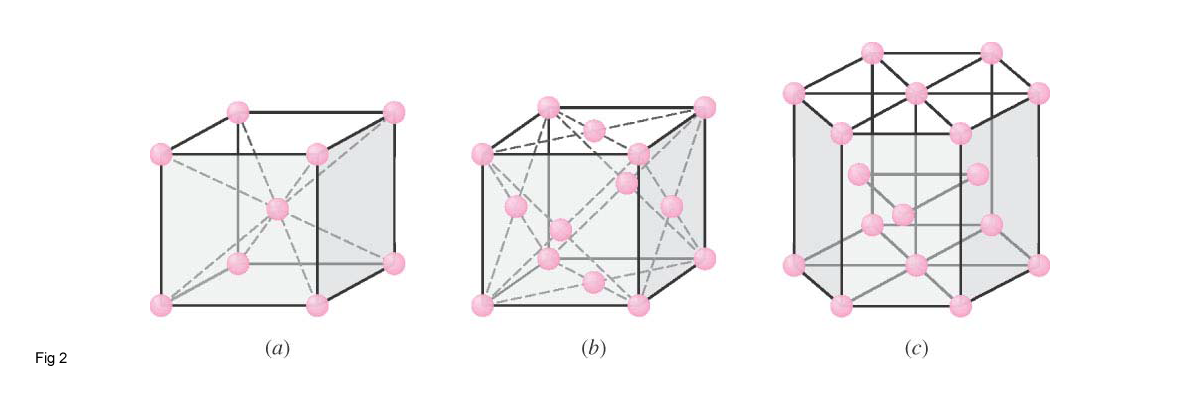
There are three principle crystal structures for metals (fig2):
- Body-centered cubic (BCC)(a)
- Face-centered cubic (FCC)(b)
- Hexagonal close-packed (HCP)(c)