CERAMICS & GLASSES
Ceramics- glass are fine-grained polycrystalline Inorganic materials are typically compounds, such as metal oxides, carbides, or nitrides. They formed when Ceramics- glasses of suitable compositions are heat treated and thus undergo controlled crystallisation to the lower energy, crystalline state. They possess many interesting properties, which can also differ structurally from other types of materials like metals and polymers. They have the following characterisations such as:
- Resistant to high temperature creep
- Corrosion and oxidation resistant
- High hardness
- Low to moderate density compared to metals
- High modulus of elasticity (stiffness)
- Good strength retention at elevated temperatures
- Dimensional stability
- High compressive strength
- Low to moderate tensile and shear strength
- Good electrical insulation properties
- Wide range of thermal conductivity
- Wide range of thermal expansion coefficient
- Low impact strength
- Sensitive to thermal shock
STRUCTURE
Most crystalline inorganic compounds are based on nearly close-packing of the anions (generically referred to as O or X, though oxygen is the most common anion) with metal atom cations (generically called M or A) placed interstitially within the anion lattice. The compounds NaCl, MgO, MnS, LiF, FeO, and many other oxides such as NiO and CaO have the so-called rock salt structure, in which the anions, such as Cl or O, are arranged in an FCC array (fig1), with the cations placed in the octahedral interstitial sites, also creating an FCC array of cations. For example: When (neutral) atoms such as sodium (metal) and chlorine (nonmetal) are ionized, the sodium loses an electron and the chlorine gains an electron (fig1):
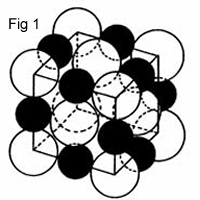
Na = Na+ + e
Cl + e = Cl-
Thus, the sodium and chlorine are able to make up an "ionic compound" by the strong attraction of the positive and negative ions. The negatively charged ions are much larger due to the gain and loss of valence electrons than the positively charged ones. The NaCl has a face-centered cubic (fcc) structure, where the positive (Na+) and negative (Cl–) ions are surrounded by 6 oppositeions (CN = 6). This is called a rock salt structure; MgO, CaO, SrO, BaO, CdO, MnO, FeO, CoO, and NiO belong to the same group.The difference between these structures is due to the relative size of the ions (minimum radius ratio). Cubic zirconia (ZrO2) has an fcc packing of the Zr4+ ions and O2– ions occupying the octahedral sites. Some ceramics have covalent bonds as their primary chemical bonding force, e.g., diamond and silica. Oxygen and Silicon are the most abundant elements in Earth's crust. Their combination (silicates) occur in rocks, soils, clays and sand. The bond is weekly ionic, with Si4+ as the cation and O2- as the anion. rSi = 0.04 nm, rO.= 0.14 nm, so rC/rA = 0.286. The coordination number = 4, that is tetrahedral coordination.

