Blister Copper
The purpose of converting matte to blister copper with a grade (98-99.5%Cu) is to remove sulphur , iron and other impurities from matte. Matte from smelting process contains as major components sulphur, copper and iron, it contains major and minor amounts of metals as follow :
Cu = 30-55%, Fe = 30-45%, S=20-30%, O2=2-3%, As=0-0.5, Bi=0-0.1%, Pb=0-5% Sb=0-1%, Zn=0-5%, Ag=0-0.1%, Au=0-15*10-4 %
In the past time for producing copper, the matte was totally roasted and the product was according to the following redaction:
2Cu2O + Cu2S = 6Cu + SO2
But today this process is not used and the matte will be almost converted to blister copper in in two different steps:
- Step1: The oxidation of iron sulfur with production of slag
- Step2: The oxidation of copper sulfur and production of blister copper.
Step 1:
In this step the molten matte is charged to the converter from top of the converter and the air is blown into the matte via tuyeres along the length of the vessel.After the air is blown the iron sulphur will be oxidized to FeO,Fe3O4 and SO2. The melting point of FeO is 1385oC and Fe3O4 is 1597 oC therefore silica as flux is added. According to the following reaction it will be produced fayalite (2FeO.SiO2) which is liquid at a process temperature about 1200 oC.
SiO2 + 2FeO = 2FeO.SiO2
This slag-forming stage is finished when the matte contains about less than 1% FeS. This step called iron removal because most iron will be removed from the matte in this step.
Step2:
After removing slag, the air will be blown into the molten which contains white metal Cu2S. According the following reaction, Cu2S is converted to the blister copper.
Cu2S + O2 = 2Cu + SO2
Cu2S + 3/2O2=Cu2O + SO2
Cu2S + 2Cu2O = 6Cu + SO2
In Figure 1, the composition moves along the Cu2S-Cu line from the copper I sulphide to crude metallic copper .Probably there are three steps in the copper making stage:
- Step 1: When air is blown through the Cu2S; Sulphur is removed as SO2 and copper will stay as Cu2S1-X.
- Step2: Blowing of air regarding Figure 1, causes a second liquid phase of blister copper with 1.2% S.
- Step3: At this position the sulphide phase is disappeared and only the blister copper is remained
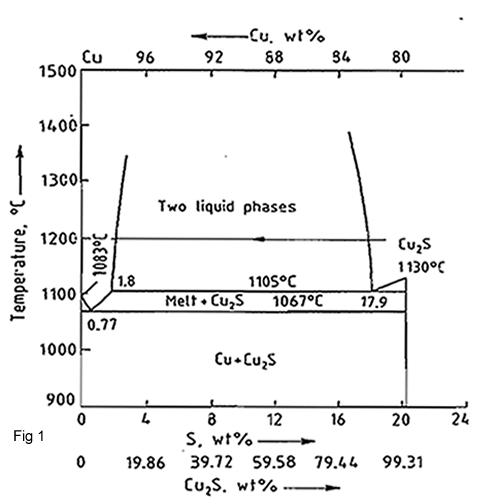
The sulphur will be oxidized by air to SO2.Copper is not oxidized until the sulphur removal has done but the air blowing process will be stop when the sulphur is about 0.02-0.1%S and the oxygen is about 0.5-0.8%O.
In industrial operations, the matte is added to the converter in two steps. After each steps the slag will be poured from converter and new matte is added and the air will be blown in the molten. The final slag can contain up to 6-15%Cu, therefore the slag will be used by matt melting process as feed or the copper will be recovered by a separate melting process or flotation process.
Technology of Converter
There are several converter types in operation but the most important of them is Piece-Smith as follows:

