Roasting
The purpose of roasting is to oxidise the sulphide contain of the concentrate but it depends of the method which will be used :
- In Pyro metallurgy; the proportion of sulphur in the charge will be reduced to a point sufficiently rich matte may be obtain. In many smelting process this sulphur will be used as a source of energy. Therefore the roasting process will be not acquired.
- In Hydro metallurgy; the sulphide minerals of copper are not easily leached but its oxides are soluble in water and its sulphates are soluble in dilute sulphuric acid
The chemistry of roasting is very complicated and could cause many different reaction but the main reactions during roasting process are the oxidation of copper and iron, sulphides to sulphates and oxides. Some reaction could be as follow:
2 MeS + 3 O2 =2 MeO + 2SO2
CuFeS2+ 4 O2 = CuSO4 +FeSO4
2CuFeS2 +7O2= CuO.CuSO4 + Fe2O3 + 3 SO2
6CuFeS2 + 13 O2 = 3 Cu2S + 2 Fe3O4 + 9 SO2
2 CuFeS2 + 6 O2 = Cu2O + Fe2O3 + 4 SO2
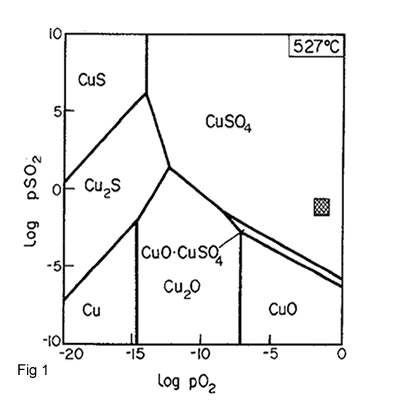
Figure 1 shows the roast products by different PSo2 and PO2 at a temperature of 527 oC .In this figure the shaded square indicates the range of partial pressures in industrial roaster gases.
Technology of Roasting:
There are several types of furnaces for roasting but usually two methods will be used more in the industries:
- Multiple-hearth roaster
- Fluid -bed roaster

