Extrusion
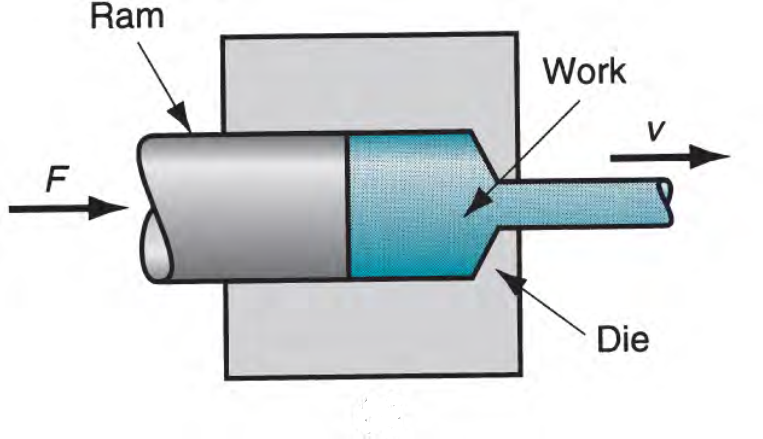
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile. A material is pushed through a die of the desired cross-section. It means that Manufacturing process in which a softened blank of a metal or plastic material is forced through a shaped metal piece or dies to produce a particular shape (fig 1).
Cold Extrusion
Cold extrusion is the process done at room temperature or slightly elevated temperatures. This process can be used for most materials-subject to designing robust enough tooling that can withstand the stresses created by extrusion. Examples of the metals that can be extruded are lead, tin, aluminium alloys, copper, titanium, molybdenum, vanadium, steel. Examples of parts that are cold extruded are collapsible tubes, aluminium cans, cylinders, gear blanks.
Hot Extrusion
Hot extrusion is done at fairly high temperatures, approximately 50 to 75 % of the melting point of the metal. The pressures can range from 35-700 MPa. Due to the high temperatures and pressures and its detrimental effect on the die life as well as other components, good lubrication is necessary. Oil and graphite work at lower temperatures, whereas at higher temperatures glass powder is used.
Typical parts produced by extrusions are trim parts used in automotive and construction applications, window frame members, railings, aircraft structural parts.

