Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Hot Isostatic pressing is a production of unique benefit in the precision, powder metal, and metal bonding and ceramics industries. It is a process in which components are subjected to the simultaneous application of heat and high pressure in an inter gas medium. The pressure is uniform in all directions or isostatic. Hot isostatic pressing (HIP) is a form of heat treatment that uses high pressure to improve material properties. That pressure is applied by an inert gas, usually argon. Time at elevated temperature and pressure allows plastic deformation, creep and diffusion to occur. Castings for critical applications are HIPed to eliminate internal microporosity thereby improving mechanical properties by removing defects. Hot isostatic pressing also enables the bonding, or cladding, of two or more materials together, either in the solid or powder form.
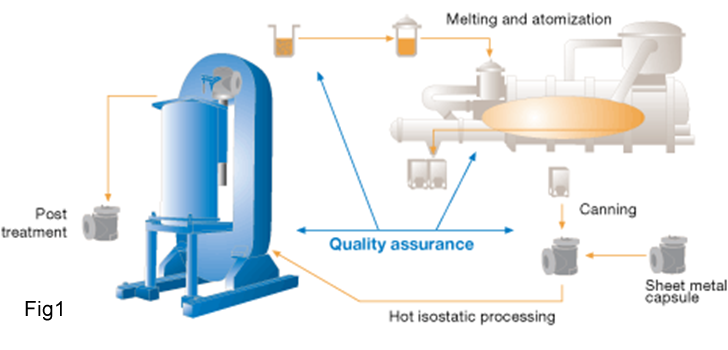
The production process from the melt to the finished product takes place in three stages. Powder is produced by inert gas atomization. The powder is canned in sheet metal capsules, giving the product the desired shape. The capsules are then consolidated into full density under high pressure and temperature by hot isostatic pressing (HIP)(fig1):
- Step 1: Melting and atomization
- Step2: Canning
- Step3: Post treatment
The melt produced in an induction furnace is tapped into an induction-heated ladle where further alloying elements can be added in a protective atmosphere. The ladle also permits stirring and temperature control of the melt throughout the process. When the melt is tapped from the bottom of the ladle it is discharged directly into the atomization chamber. The molten steel is broken up by jets of inert gas and the atomized melt solidifies into small spherical particles of high purity and low oxygen content and with a diameter less than 500 micron. The powder is stored under inert gas hermetically-sealed vessels.
The powder is canned in capsules of mild steel, which are produced by sheet metal forming and welding. The capsule is designed to give the fully dense end product the desired shape. Compound products can be produced by designing capsules with separate compartments for different powders or enclosing parts of solid material together with the powder.The capsules are placed in a hot isostatic press where they are subjected to high pressure and temperatures. The hot isostatic pressing parameters of pressure, temperature and time are predertermined to give the material full density. Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a process to densify powders or cast and sintered parts in a furnace at high pressure (100-200 MPa) and at temperatures from 900 to 1250°C for example for steels and superalloys. The gas pressure acts uniformly in all directions to provide isostropic properties and 100% densification.
Depending on the type of material and the application, the PM HIP products will be heat treated, machined and subjected to various types of quality control, such as ultrasonic inspection, dye penetrant testing, testing of mechanical properties.
The mild steel sheet used in the can remains on the product after the hot isostatic pressing and heat treatment and is removed by machining or by acid pickling.