Forging
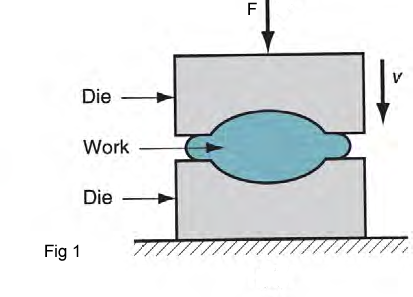
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compressive forces (fig 1).The blows are delivered with a hammer (often a power hammer) or a die (a device for cutting or molding metal into a particular shape). At its most basic level, forging is the process of forming and shaping metals through the use of hammering. The process begins with starting stock, usually a cast ingot (or a "cogged" billet which has already been forged from a cast ingot), which is heated to its plastic deformation temperature, then upset or "kneaded" between dies to the desired shape and size
Forging is often classified according to the temperature at which it is performed: cold forging (a type of cold working), warm forging, or hot forging (a type of hot working). For the latter two, the metal is heated, usually in a forge. Forged parts can range in weight from less than a kilogram to hundreds of metric tons. Forging has been done by smiths for millennia; the traditional products were kitchenware, hardware, hand tools, edged weapons, and jewellery. Since the Industrial Revolution, forged parts are widely used in mechanisms and machines wherever a component requires high strength; such forgings usually require further processing (such as machining) to achieve a finished part. Today, forging is a major worldwide industry.

